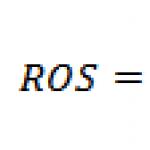Find out information on the limit. The practice of checking a counterparty for good faith: how to avoid tax claims. What documents are most often requested when checking a counterparty?
- full and abbreviated name of the organization in Russian (also, in some cases, company name in English language),
- organizational and legal form of the legal entity,
- legal address ( location),
- information about the status of the legal entity,
- management of the organization (information about persons who have the right to act on behalf of a legal entity without a power of attorney),
- information about the founders (participants),
- information about the register holder (for joint stock companies),
- size authorized capital organizations,
- information on the size and nominal value of shares in the authorized capital of the company belonging to the company and its participants,
- information on the transfer of shares or parts of shares as collateral or on their other encumbrance,
- information about the person managing the share transferred by inheritance,
- information about branches and representative offices,
- information about the types of activities of the organization (main and additional),
- information about issued licenses,
- information about being in the process of reorganization,
- information about being in the process of liquidation,
- method of terminating activities for liquidated legal entities,
- information about succession - for legal entities created as a result of the reorganization of other legal entities, for legal entities, in constituent documents which changes are made in connection with the reorganization, as well as for legal entities that have ceased their activities as a result of the reorganization,
- taxpayer identification number (TIN) and information about registration with the tax authority,
- information about registration as an insurer with the territorial body of the Pension Fund Russian Federation(PF RF) and in executive body Fonda social insurance Russian Federation (FSS RF),
- information that the legal entity is in the process of reducing its authorized capital,
- the date of registration of changes made to the constituent documents, or, in cases established by law, the date of receipt by the registering authority of notification of changes made to the constituent documents.
An extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities is an excerpt of basic information about a given legal entity (with the exception of some personal data about individuals ah, which are provided only to authorized bodies) from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
Unified State Register of Legal Entities (USRLE) - federal information resource, containing general systematized information about all legal entities engaged in entrepreneurial activity on the territory of the Russian Federation, as well as, in a number of cases, about liquidated organizations and those in the process of liquidation. The register is maintained by the Federal Tax Service of Russia (FTS RF) through territorial bodies. In accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, Unified State Register of Legal Entities data is open and publicly available.
The information contained in the extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities is key when checking the counterparty and, along with other documents, can confirm ownership, the rights of the founders or management of the organization to conclude contracts and perform other legally significant actions on behalf of a legal entity (LE), and also provide valuable information about the state of the legal entity and the overall reliability of the counterparty.
There are several main types of statements:
Regular (electronic, informational) extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities– contains basic open and publicly available information from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. It does not contain passport data of the founders and managers of the legal entity, as well as information about the organization’s bank accounts.
You can get an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities online and completely free of charge on the website, the data is updated daily from the official source (Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation), the document will be completely identical to the extract that you can download on the official tax website (egrul.nalog.ru). The information is always up to date as of the current date.
Extended statement– contains full information, including passport details of the participants of the legal entity and its director. It is provided only to authorities, courts, government off-budget funds. Such a document is also provided by the tax authority to a legal entity or its representative about itself.
Official extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities– a document certified by the seal of the Federal Tax Service and received from the tax authority. It is a numbered and stitched printout on several sheets with the stamp of the tax authority.
Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN, read as "ienen") is a special digital code that is issued to individuals and legal entities in order to streamline and control the payment of taxes.TIN plays one of the main roles in the individualization of legal entities and individuals with the status individual entrepreneur(IP) as taxpayers.
Check the TIN and get information about the counterparty
TIN of legal entity and individual entrepreneur
Entity receives a tax identification number from the tax authority at the place of registration of the person simultaneously with other registration documents.Individuals with individual entrepreneur status can obtain a TIN in two ways:
1) simultaneously with the assignment of individual entrepreneur status and the issuance of a certificate of registration as an individual entrepreneur;2) at any time before registration as an individual entrepreneur (in this case, upon registration There is no need to get a TIN again).
Without a TIN, an individual will not be able to obtain individual entrepreneur status.
Legal entities and individuals with the status of individual entrepreneurs, when concluding any agreements, are obliged indicate your TIN in the details.
The TIN must be located on stamps (for individual entrepreneurs - if there is a stamp).
TIN of an individual without individual entrepreneur status
Individual can obtain a TIN from the tax authority at the place of residence.Currently obtaining TIN by individuals is voluntary. Exception: TIN is required for an individual when appointing him to the position of a civil servant.
In practice, when applying for employment in other positions, they are often asked to present the TIN along with other documents. Such a requirement cannot be mandatory, since it is not reflected in Labor Code RF.
TIN verification
Anyone can visit our website for free check the correctness of the TIN counterparty - a legal entity or an individual with the status of an individual entrepreneur, as well as the fact of making an entry on the registration of a legal entity in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.Knowing the TIN and the name of the organization, you can obtain an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities for verification:
- the reliability of documents received from the counterparty (since legal entities and individual entrepreneurs are required to indicate the TIN on any local acts and documents they issue);
- the fact of the existence of a legal entity (situations are possible when an unscrupulous counterparty, for selfish purposes, acts in a transaction on behalf of a non-existent legal entity);
- the reliability of the counterparty's legal address;
- last name, first name and patronymic of the director of the legal entity and other information about the legal entity.
An individual can, via the Internet, and knowing the TIN - the amount of debt for taxes and fees. TIN verification individuals is carried out free of charge online.
Verification of the counterparty: procedure in questions and answers
Verifying a counterparty by TIN is a mandatory procedure that all business representatives face sooner or later, regardless of their line of business. Is it worth cooperating with a counterparty, is it possible to trust him and make an advance payment? This is only a short list of questions that can be answered by carrying out a procedure such as checking the counterparty by TIN.
If we consider individual situations, the need to check the counterparty can be useful to an accountant who wants to make sure of the transparency of the activities of a potential partner of his company before concluding an agreement. By using the TIN number on our website you can obtain an extract about the legal entity from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, as well as expanded financial data on the legal entity.
It will be rational to present basic information about conducting a verification of a counterparty by TIN in the form of questions and answers in order to achieve high degree understanding the need for this procedure and the features of its implementation.
What is verification of a counterparty by TIN?
Checking a counterparty by identification number includes a search for information about him and its further analysis aimed at determining the integrity/bad faith of a potential partner.
Who is responsible for checking counterparties?
In most cases, checking the counterparty by TIN is the responsibility of employees legal service And economic department. If such structural divisions the enterprise does not, responsibility for checking the counterparty will be borne by the person authorized to conclude the contract.
Why do you need to check your counterparty?
The verification of the counterparty is carried out to minimize financial risks from cooperation with him. Analysis of data obtained using the Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) will help avoid delays in deliveries, problems with the quality of goods or services, and will make it possible to stop fraudulent schemes of the counterparty.
In addition, this check is necessary to avoid sanctions from the tax authorities: if violations are found, then responsibility for choosing a counterparty will fall entirely on your organization. The consequences may be different (exclusion of a transaction of a dubious nature from expenses, refusal to accept VAT for deduction), so it is imperative to check the counterparty.
What exactly is studied when checking a counterparty?
The specifics of checking a counterparty - the procedure, responsibilities of the parties, the criteria by which research is carried out - are not established at the legislative level. The concept of “counterparty verification” on this moment is not prescribed in regulations and is absent from the Tax Code.
Along with this, in 2006, a Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court RF, which somewhat clarifies who should check the counterparty. It is devoted to the issue of assessing the validity of a person receiving a tax benefit. It may be found unfounded in court if it turns out that the taxpayer acted imprudently. In practice, this means that responsibility for checking the counterparty rests with business representatives. In fact, in most cases the audit is carried out by accountants.
What documents are most often requested when checking a counterparty?
The absence of a written counterparty verification scheme somewhat complicates the process. At the same time, a standard practice has already developed, which involves collecting and studying such documents of the counterparty as the charter, an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, certificates of state registration and registration tax accounting, a letter from statistics indicating activity codes, documents identifying the counterparty and confirming his authority.
The privacy policy (hereinafter referred to as the Policy) has been developed in accordance with Federal law dated July 27, 2006. No. 152-FZ “On Personal Data” (hereinafter referred to as FZ-152). This Policy defines the procedure for processing personal data and measures to ensure the security of personal data in the vipiska-nalog.com service (hereinafter referred to as the Operator) in order to protect the rights and freedoms of humans and citizens when processing their personal data, including the protection of rights to integrity privacy, personal and family secrets. In accordance with the law, the vipiska-nalog.com service is for informational purposes and does not oblige the visitor to make payments or other actions without his consent. The collection of data is necessary solely to communicate with the visitor at his request and inform him about the services of the vipiska-nalog.com service.
The main provisions of our privacy policy can be formulated as follows:
We do not share your personal information with third parties. We do not transfer your contact information to the sales department without your consent. You independently determine the amount of personal information disclosed.
Information collected
We collect personal information that you have knowingly agreed to disclose to us in order to obtain detailed information about the company's services. Personal information comes to us by filling out a form on the website vipiska-nalog.com. In order to receive detailed information about services, costs and types of payments, you must provide us with your email address, name (real or fictitious) and telephone number. This information is provided by you voluntarily and we do not verify its accuracy in any way.
Use of the information received
The information you provide when filling out the questionnaire is processed only at the time of the request and is not saved. We use this information only to send you the information you signed up for.
Providing information to third parties
We take protecting your privacy very seriously. We will never provide your personal information to third parties, except as may be expressly requested. Russian legislation(for example, at the request of the court). All contact information you provide to us is disclosed only with your permission. Email addresses are never published on the Site and are used by us only to communicate with you.
Data protection
The Site Administration protects information provided by users and uses it only in accordance with the accepted Privacy Policy on the Site.
To legally conduct business, all organizations are required to obtain a TIN. With its help, fiscal authorities record and control tax revenues. And other participants market relations can use the TIN to verify the legality of activities or any kind of debt to the state.
TIN of a legal entity
TIN - individual taxpayer number. All economic entities registered on the territory of the Russian Federation (individual entrepreneurs, organizations and enterprises, farms and commercial funds) have it.
TIN of legal entities - a sequence of 10 digits according to the general classifier tax accounting. Each number or combination thereof represents a certain code by which you can obtain information about the taxpayer:
- 1-2: code of the subject of the Russian Federation;
- 3-4: tax office number;
- 5-9: taxpayer number in the Unified State Register.
The TIN code is unified throughout Russia. Assigned to the taxpayer once.
Important. In the event of a change in the personal data of the manager (change of last name or registration address), the law does not provide for any action on the part of the organizer. That is, the enterprise is registered using the code created initially. The TIN must be replaced only when the organizational and legal form of the company changes (OJSC, CJSC, LLC, Individual Entrepreneur) or its reorganization. When changing the address and name, you only need to notify the tax office to receive correspondence at the correct address.
All counterparties, in accordance with the code designation, are divided into:
- Legal entities (residents);
- Individual entrepreneurs;
- Foreign legal entities (non-residents).
You can find reliable information about a functioning enterprise using the online service of the Federal Tax Service (FTS) and other government agencies.
Knowing the TIN number allows you to:
- Clarify information on companies with the same names (city, owner);
- Track the amount of tax contributions of the company to the Pension Fund;
- Establish the fact of tax registration;
- Identify unscrupulous partners;
- View your total tax debt;
- Make a duplicate of the lost tax registration certificate (TIN) and compare it with the number of the previous one (identical);
- Make a bank transfer to the company's account;
- Find out the city where tax registration was carried out, the full name of the manager and his registration address, legal information about the organization (address and name);
Check the validity of the TIN in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities on the page egrul.ru/test_inn.html
There are situations when an organization’s TIN needs to be found out quickly. And there is no way to find out the code directly.
In this case, the following resources can help:
- egrul.nalog.ru (according to OGRN);
- fek.ru (according to any data);
- fedresurs.ru (by company name or full name);
- Through browser search.
Find an organization by TIN on the tax website
- Follow the Federal Tax Service link to free service by TIN verification.
- There is a form in the center of the page. In it you need to select the data on which the verification will be carried out (OGRN/TIN or name of the enterprise).
- If the search is carried out using INN/OGRN, the system displays the only result, corresponding to the taxpayer ID code. If the search is carried out by name (name) or full name, the system produces a list of enterprises (entrepreneurs) that meet the search criteria.
- To get the result, you must enter the digital captcha code shown in the picture in a special window.
- Next, click on the “Find” button.
Important. The search result by TIN returns the only organization registered with this code.
Check the organization by TIN on the tax website
This is necessary before concluding a contract, signing contractual obligations or other formal agreements with the counterparty. You should always first check the reliability of the legal entity, its financial position and reliability rating.
You can check your counterparty by TIN on the tax office website for free in the following way:
- Without registering;
- With registration of a personal account.
The choice of method depends on the purpose of the check. If an officially certified document is required, the application must be submitted through your personal account. After processing the request, the system redirects the user to the statement page. The information is presented in table form.
- It reflects the following data:
- Full name of the legal entity with the Federal Tax Service report in PDF format;
- Registration address of the legal entity (postal code, city, street and building);
- Main state registration number(OGRN);
- Registration reason code (KPP);
- Date of assignment of the OGRN;
- Date of termination of activity;
- Number of registration invalidation.
Important. The service makes it possible to obtain an extract from electronic signature tax authority also in PDF format (Adobe Reader). To do this, you need to register on the Federal Tax Service website and submit an application. The service is provided free of charge.
Logging into a taxpayer’s personal account on the nalog.ru website is possible only by personally contacting the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate (the nearest branch). Registration is possible for legal entities and individuals (IP).
To access your account you need:
- Write an application for access to personal account taxpayer;
- Fill out the registration card. To do this, you need to take your TIN and passport (originals) with you;
- Receive an individual login and password, which can later be changed;
- Complete online home registration by activating your data;
- Request an extract about the counterparty.
Important. Need to create email to complete the application. Her address will be used by the tax office for the exchange of correspondence.
The Federal Tax Service report is an extract from a single state register legal entities (USRLE). Contains complete information about the organization, presented in tabular form on several A4 sheets.
The report allows you to find out the following data:
- Name of the organization;
- Location;
- Company registration information;
- Information about tax registration;
- Insurance information ( Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund);
- The amount of authorized capital;
- Circle of persons with trust management;
- Information about founders or participants;
- Kinds economic activity according to OKVED;
- Data on availability of licenses;
- Data on records from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
Checking data about the counterparty allows you to assess its legal capacity and the possibility of applying tax deductions and benefits in case of concluding a contract. If an organization is not listed in the database, then it operates illegally.
What to do if you couldn’t check your counterparty on the tax website
The lack of data about the counterparty in the Federal Tax Service databases is due to two factors:
- Error entering digital code;
- Illegality of a legal entity.
If the TIN was obtained from unofficial sources, you should double-check the data and find the correct TIN (by company name or address).
Important. The service allows you to carry out a similar check. These checks allow you to find out the TIN, full name of the organization and city of registration.
If the TIN was received directly from the counterparty, you must request a package of documents for a more thorough check:
- A copy of the state registration certificate;
- Tax reporting for the previous period with the seal of the Federal Tax Service;
- A copy of the tax registration certificate;
- A copy of the director's passport and statutory document etc.
A thorough analysis of the company in the event of litigation will play in favor of the plaintiff. He exercised due diligence in the absence of any data from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. For example, when signing preliminary agreement for the provision of services.
Algorithm of actions in case unsuccessful attempt is:
- First, the TIN is checked for validity;
- Determine whether the company is actually registered as an economic entity. To do this, make an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs;
- Check accounting information and balance. Their authenticity will be evidenced by economic activity and availability of funds for payment;
- Compare the actual and legal address. To assess the reliability of the counterparty, a site visit may be required to assess the realities;
- They check the “black list” of the Federal Tax Service, called the “List of Disqualified Persons”.
Important. Disqualification is a temporary restriction on the management of a company. The list of disqualified companies includes companies engaged in fraud (fictitious bankruptcy, concealment of property, forgery of documents) or other types of illegal activities.
In addition to checking by TIN, the tax website allows you to include this or that organization in special registers.
Receiving information in the form of statements on them is paid.
Support
If you have questions related to the operation of the service, use the form to contact the support service.
Information in the Federal Tax Service databases is updated daily. If the service does not return search results (does not function), you should contact technical support. If you have any other questions, please contact the call service.
To apply, you need to find the appropriate section by following the instructions on the link. When moving to the next page, you should indicate from which person the appeal is being made (legal or individual / individual entrepreneur).