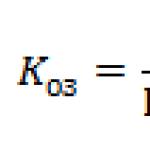Rules for calculating and accruing compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal. What is compensation for unused vacation? How to correctly arrange cash payments instead of required rest? Compensation for unused vacation how many days
You can’t work without vacation, just as you can’t work without lunch breaks or weekends.. This is prohibited by both common sense and legislation. For every honestly worked year, according to the Labor Code, there are 28 vacation days.
And in case of harsh working conditions or a specific specialty of the employee, the legislation not only allows, but also obliges the employer to provide additional days off.
But what to do if you couldn’t take a break from work for some reason? Is there compensation for unused vacation?
The Labor Code provides in this case there are 3 options when unused vacation can be replaced with monetary compensation:
- Receive monetary compensation for unused allotted rest upon dismissal or retirement, provided that the duration of the vacation does not exceed 28 days.
- Receive compensation in cash equivalent, if provided.
- Use non-vacation time off.
The principle for calculating the amount of monetary compensation is reflected in Resolution 922 of the Russian Government (dated December 24, 2007).
The amount of vacation pay and compensation for them directly depends on the amount of official income - salary, bonuses for the 12 months preceding legal vacation or dismissal (retirement).
Example: a woman worked at the enterprise from May 1, 2014, after which, in 2016, she was transferred to another organization. During the entire period of work, the woman never used her vacation and therefore now she is entitled to compensation.
The employee's income for the 12 months before the transfer was as follows:
- November 2015 – 10,000 rubles.
- December 2015 - 10,000 rubles.
- January 2016 - 10,000 rubles.
- February 2016 - 10,000 rubles.
- March 2016 - 10,000 rubles.
- April 2016 - 10,000 rubles.
- May 2016 - 10,000 rubles.
- June 2016 – 6316 rubles, vacation starts from June 20.
- July 2016 – 0 rubles.
- August 2016 – 0 rubles.
- September 2016 – 0 rubles.
- October 2016 - 0 rubles.
No bonuses awarded. The total income was 76,316 rubles.
Now you need to decide on the billing period:
- Fully worked months – 7.
- The average number of days in months worked is 29.3.
- Days worked in June – 19.
- The number of days in June is 30.
It turns out: 7*29.3+19*29.3/30 = 205.1+18.56= 223.66 days.
 Average daily income is defined as the sum of total income divided by the number of days in the billing period:
Average daily income is defined as the sum of total income divided by the number of days in the billing period:
76316 /223.66 = 341.21 rubles.
For the entire period of work from 2014 to 2016, the woman was entitled to 69.4 days of legal rest.
Since, according to the Labor Code, the average daily pay is maintained for each vacation day, the compensation will be: 341.21 * 69.4 = 23,679 rubles 97 kopecks.
If the employee was undergoing training, sick leave, business trip, and he was compensated for his expenses, then these amounts cannot be counted as income and are not taken into account when calculating payments.
Important! If the vacation was not used in full, or days of additional time off were not used, then calculation is carried out based on the actual remaining days.
Taxation
What are vacation pay or compensation for them? This is essentially the same income as wages. Is there a fee? The organization is subject to taxation on all employee income. ?
IN due to personal income tax accruals, the employee receives 13% less. This interest will be sent to the tax office as income tax. The amount of deductions for insurance premiums and the pension fund depends on the amount of compensation. But they are paid from the employer’s income and amount to 30% of the accrued compensation to the employee.
The Tax Code tells in more detail about the amounts of withheld amounts (Article 208, ,), 167th Federal Law And 184th Government Decree.
About breaking the law
 Now about the painful part.
Now about the painful part.
The problem that many leaving employees face is did not pay compensation.
This is a gross violation of Labor legislation and, on the basis of which the resigning employee carried out his activities and is equivalent to non-payment of wages.
If you suspect that something has not been paid extra, pay attention to the 2-NDFL certificate. Upon dismissal, the accountant is required to issue this document. The certificate reflects all income, including vacation pay and compensation for it.
If there are no accruals for unused vacation, you need to do the following:
- Write a complaint to the employer with a demand for payment of compensation for unpaid vacation.
- Contact the Labor Inspectorate with a statement about the violation of your rights. This can be done by sending an electronic application, a paper application or during a personal visit to the inspectorate. Your application will be considered within 30 days. During this period, Employees Labor. The inspectors will make a request to your employer, find out the reason for non-payment and inform you in writing about the results of the inspection.
- Contact the Prosecutor's Office. This appeal can be combined with an appeal to the Labor Department. In the name of the Prosecutor of where the employer's organization is registered - i.e. according to legal address you need to write a statement with a complaint about the violation of your rights according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation by the former director. The prosecutor's office will also conduct an investigation within a month.
- Going to court. Unlike the Labor Inspectorate and the Prosecutor's Office, the court will not be able to hold the employer accountable. But it is quite possible to oblige him to pay everything due to the employee. The statement of claim also indicates violated rights and demands to recover compensation from the former bosses for unused vacation. After a decision is made on the basis of the writ of execution, the employer’s accounts will be seized and everything that he did not pay in addition will be paid to the employee.
About responsibility
 Any delays in payments at the enterprise threaten management with the need to pay interest.
Any delays in payments at the enterprise threaten management with the need to pay interest.
In a situation with vacation pay and compensation for them, the director bears not only the obligation to pay the main amount, but also for each day of delay at least 1/300 of the current refinancing rate.
That is, the employer is financially obliged.
In addition, unscheduled inspections by the tax service and the Prosecutor's Office may be organized in relation to its activities.
Despite the fact that vacation was invented to make life easier for the working population, not everyone uses it. We hope the information provided in the article will help you receive compensation for unused vacation.
Useful video
Is it possible to pay compensation for unused vacation? In what cases is this possible? How to apply correctly? You will learn about this in the following video:
Every employee can count on benefits upon dismissal. When this will be only a refund of unused vacation days, and when larger amounts are due, we will explain in the article.
Read in the article:
Labor Code: compensation upon dismissal
According to Art. 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, on the day of leaving work, the employee must receive all amounts due to him. This list consists not only of money earned over the last month, but also compensation payments. Their size and list depend primarily on the reason for termination of the contract.
Meeting the deadlines for issuing money is a priority for the company. After all, an inspection of the State Tax Inspectorate, which comes within a year, will certainly punish the unscrupulous employer (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). And not only will he impose a fine, but it can reach 50,000 rubles. for legal entities, but will also force them to pay compensation for the delay in transferring amounts. Its size will be 1/150 of the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of transfer for each day of delay.
And if delays in a company are widespread, then a fine will be imposed for each individual case, which will result in a hefty sum for the employer. If the delay is longer (more than 3 months), criminal liability may arise for the manager (Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Early dismissal
When liquidating or downsizing, the company must warn staff about the impending changes. This procedure is carried out at least 2 months before the expected date of termination of the contract. Moreover, even before the expiration of the notice period, the contract can be terminated with the consent of the worker.
For the entire period before the initially planned date of departure, the employee is paid a salary based on the average monthly income.
Content
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, any employed citizen has the right to guaranteed annual paid rest. Its duration is 28 days or more. Under certain circumstances, it is possible to increase its duration. If additional days of rest are not used, the employee can apply for financial compensation. The conditions for its provision are regulated by federal legislation.
What is monetary compensation for unused vacation?
All employed citizens have the right to annual leave, but not every employee uses it fully. Paid vacation days, the number of which exceeds 28, are subject to transfer or financial compensation - at the employee’s choice. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility of receiving cash payments only in exchange for additional days off.
In case of dismissal of an employee, upon calculation, on the last working day, the employer is obliged to pay him compensation in proportion to the period of time worked in the organization. Payment for the remaining days of rest in cash is made upon written request from the employee. The procedure for paying compensation for unused vacation is regulated by federal regulations and legislative acts.
Who is not entitled to compensation payments
There are restrictions on the circle of persons who have the right to replace unused vacation periods with cash payments. Article 126 of the Labor Code prohibits the provision of compensation for part of the vacation period:
- main and additional – for pregnant women and employees under 18 years of age;
- additional – for persons working in difficult, harmful, dangerous conditions.
Reasons for taking leave without leave
If an employee has written an application for full annual compulsory rest, but due to certain circumstances it was not possible to use it completely, days arise in return for which you can receive monetary compensation. The reasons for this situation may be:
- illness – receipt of a certificate of temporary incapacity for work, with a maximum duration of 30 days, for the period of which the annual compulsory rest is extended;
- the manager’s decision to recall the employee from leave due to production needs;
- transfer of the vacation period at the initiative of the employee due to valid reasons, for example, the death of a relative;
- the amount of vacation pay for the billing period was incorrectly calculated;
- performance of government duties during the annual holiday that involve release from work.
Legal regulation
Payment of compensation for unused vacation is made at strictly specified times by law. Most of the nuances are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- Art. 126 – monetary compensation for vacation days exceeding the standard 28;
- Art. 127 – the same, but upon dismissal;
- Art. 115–120 – duration of main and additional leave;
- Art. 423 – on the proportionality of the amount of funds received in return for unused vacation days;
- Art. 251–351 – features of regulation of working and rest conditions of certain categories of citizens.
The right of representatives of certain professions to receive monetary compensation in return for unused vacation is established by Part IV of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and ministerial letters and orders. The procedure for calculating length of service, calculating the number of days due for compensation and other nuances are regulated by the following regulations:
- Rules on regular and additional holidays, approved by the USSR People's Commissariat of Labor in 1930, as amended in 2010;
- Letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 4334-17 dated December 7, 2005;
- Letter of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment No. 944-6 dated June 23, 2006;
- Letter of Rostrud No. 5921-TZ dated October 31, 2008;
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 922 of December 24, 2007;
- International Convention “On Paid Holidays” No. 132 (ratified on July 1, 2010).

In what cases is compensation due?
In most cases, the entire remaining number of days of annual rest is subject to recalculation and payment upon dismissal. Situations are also possible when continuing to work in the organization. The rarity of the latter option is due to the fact that the Labor Code prohibits compensation for the basic 28 days due to the majority of the working population (with the exception of certain professions, for example, doctors, teachers, etc.), and employers prefer to transfer the rest to the next billing period.
An employee is entitled to an annual paid holiday of 28 calendar days at least once every 24 months. Failure to provide this is a violation of the law and entails administrative penalties for the employer. Having used half of the 56 days allotted for 2 years worked, the rest cannot be reimbursed in cash, because all of these are components of the mandatory main part. Replacement with money is possible only in case of termination of the employment contract. These rules apply to main employees, internal and external part-time workers.
Upon dismissal of an employee
The right to use annual paid leave arises for an employee after six months of work. Upon dismissal, all due unused vacation days are subject to compensation, regardless of the amount of time worked in the organization. For example, an employer who has worked for 4 months must compensate the period of compulsory annual rest in proportion to this period. For accurate calculation, a special formula is used.
No dismissal
If the employee continues to work at the enterprise, the vacation days not used by him during the accounting year are, with his consent, transferred to the next year or paid. Article 115 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation prohibits compensation for basic annual paid leave. If the employee does not take a full day off, he can reimburse the remaining amount, even if he does not quit, but only the amount exceeding the required 28 calendar days is subject to payment.
Excessive days are additional days provided for by law, local regulations of the enterprise, remaining days off for the previous accounting year, etc. Article 116 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for an extended duration of annual rest, in return for which compensation for unused vacation without dismissal is possible for the following categories of employees:
- having a special nature of work - the number of additional days is established by the Government of the Russian Federation;
- those employed in hazardous industries – at least 7 days;
- with an irregular schedule – 3 or more;
- having dangerous working conditions – more than 6;
- those living in the Far North and equivalent areas - depending on the regional coefficient;
- disabled people, pensioners – up to 14 calendar days;
- representatives of certain professions: doctors, teachers, researchers, civil servants;
- otherwise, if this is established by local regulations of the employer.

Calculation of compensation upon dismissal
An employee who has worked for a certain period of time and has not taken advantage of the right to annual paid leave must be compensated for these days in cash upon dismissal. The reason for terminating an employment contract - at will, expiration, violation of labor discipline, etc. - does not affect the right to receive payment; it is due to everyone. Compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal is calculated:
- in proportion to the time worked;
- taking into account average daily earnings.
When is full compensation due?
In some cases, an employee is entitled to reimbursement of unused vacation days for a full 12 months, even if the period worked is less. This happens when an employee has worked at the company for a period exceeding 11 months - 1 year and 11 months, 2 years and 11 months. etc. or has at least 5.5 months of experience and was fired for the following reasons:
- staff reductions;
- liquidation, reorganization of an enterprise, structural unit;
- redirection to another place of work;
- conscription for military service;
- professional incompetence.
Employee's vacation period
Employees are entitled to rest in the amount of 28 calendar days not for the calendar year, starting in January, but for the billing year, calculated from the date of hire. For example, an employee was employed on 02/04/2016, the calculation year for him will be 02/04/2016 - 02/03/2017 (in the absence of periods shifting it). The right to use up to 14 calendar days (more if agreed with superiors) arises for the employee after 6 months of continuous service, i.e. in the above example – 08/04/2016, and the full one can be used after 11 months. – 01/04/2017
It is possible to provide annual leave in advance to the following categories of employees:
- persons under 18 years of age;
- pregnant women;
- having children under three years of age;
- part-time workers;
- beneficiaries, for example, pensioners, disabled people, etc.
To determine the number of unused days for the purpose of compensation, it is necessary to calculate the vacation period. Vacation periods excluded from the calculation:
- without pay, lasting more than 14 days in 1 year;
- for child care up to 1.5 or 3 years.
For example, an employee employed on 02/04/2016 used 12 days of the main one and 28 at his own expense (01/08–28/09), then upon dismissal on 01/10/2016 he is entitled to compensation for the unused period 04/02–01/08 and 15/08–01/10. To round off the months that make up the vacation period, the arithmetic principle is used: 15 or more days of the last month are rounded up, shorter durations are rounded down.

Formula for calculating vacation pay
An employee can calculate the amount due for unspent vacation on his own using an online calculator, but it is difficult because you need to know your total annual income, the number of days off and the vacation period. Payment of compensation for unused vacation is calculated by enterprise accountants using the formula:
- Amount = Number of unused days × Average daily earnings.
The amount due for the rest period worked can be calculated in two ways:
- According to the Rules on regular and additional leaves of 1930, the document approved in the Soviet Union, with amendments, is still in force. Days subject to compensation = Months worked × Number of allotted days per year / 12. For example, an employee who has worked 7 months, at his request, is provided with payment for 7 × 28/12 = 16.33 = 17 days. According to the regulations of the Ministry of Health and Social Development, rounding is not performed in calculations, but if necessary, a non-integer number is rounded in favor of the employee, even if this contradicts the rules of arithmetic.
- According to the standards established by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation: 2.33 × number of months worked. For 7 months worked, 2.33 × 7 = 16.31 is calculated; when rounded towards the employee, they receive the same 17 days subject to compensation.
Average daily earnings are calculated using a formula that takes into account the salary for the year:
- SDZ = ZP / 12 / 29.3, where:
- Salary – the employee’s salary for the last 12 months, excluding sick leave payments, overtime due to production needs, and periods of forced downtime;
- 12 – number of months in a year;
- 29.3 – the average number of days in a month (this average monthly number was introduced into the Labor Code in April 2014 and remains relevant now).
If one or more months were not fully worked out, the calculation is made using a completely different formula:
- SDZ = KPM × 29.3 + NP1 + NP2 +…, where:
- KPM – number of full months,
- NP – number of days worked in incomplete month(s).
For seasonal workers and persons who have entered into a fixed-term employment contract lasting up to 2 months, the number of days of paid leave due is indicated in Art. 291 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and amounts to 2 days per month worked. The number of vacation days entitled to compensation for certain other categories of workers is indicated in Part 4 of the Labor Code.
How to get compensation
In order to receive monetary compensation for unused days of paid vacation, you must contact the accounting department at your place of work with a written application. On its basis, an order for the payment of compensation is issued, issued to the employee against signature, and the corresponding entries are made in personnel documents - personal card, vacation schedule.
Statement
The application form for payment for unused vacation has not been approved at the state level. The employee draws up a document in any form indicating the basic necessary details:
- in the header: full name, position of manager, employee;
- center: “statement”;
- from the red stock, sample text: “I ask you to pay me monetary compensation in exchange for unused days...”;
- amount of days;
- billing period;
- date, employee signature with transcript.

Order from the manager to replace vacation with monetary compensation
Having accepted the employee’s application, the manager endorses it and issues an order for the accounting and human resources departments. If the director is directly responsible for personnel records management, he is recommended to check the data specified in the employee’s application in order to avoid financial errors in calculations. There is no unified form of the order; it is created according to the standard standards of the organization, indicating the information necessary for this case - the employee’s full name, the number of unused days, etc.
An approximate version (sample document format):
Limited Liability Company "Vesna"
Vesna LLC
No. 137-ls dated 10/01/2017
Moscow
On replacing part of annual leave with monetary compensation
In accordance with Art. 126 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
I ORDER:
Senior technologist I.A. Makarova replace with monetary compensation part of the additional leave for the period 03/12/2016 to 03/11/2017 in the amount of 2 (two) calendar days.
Reason: personal statement by I.A. Makarova. from 09/29/2017
Director of Vesna LLC (signature) Kryuchkov D.S.
I have read the order:
Senior technologist (signature) Makarova I.A.
When is it paid?
Cash compensation for unused vacation without dismissal is paid on the date of payroll for the current month. Upon termination of an employment contract, the transfer is made on the last working day or on the day the employee submits demands for payment. Failure to comply with payment deadlines or evasion of fulfilling a legal obligation related to payment for unused days will entail the imposition on the employer of sanctions established by:
- Tax Code;
- Code of Administrative Offences.
Taxation and insurance premiums
Taxation of compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal is regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Article 226 obliges the employer to transfer personal income tax no later than one working day following the date of dismissal of the employee. In any situation - upon dismissal or while continuing to work - mandatory insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund and the Pension Fund are deducted from the amount paid (Federal Law No. 212, clause 2, part 1, article 9).
In the accounting documents of an organization (small enterprise) that does not have a vacation pay fund, reimbursement of unused days is reflected as an expense item (Article 225 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), therefore it affects the payment of income tax by organizations using the “income minus expenses” tax system and does not affect on those using only income as an object of taxation.

What to do if the compensation payment is not accrued or not paid on time
A delay in calculating compensation for unused days or its absence is a reason to appeal to the labor inspectorate and the court. The Code of Administrative Offenses provides for fines for employers in the amount of:
- 10–20 thousand rubles – for officials;
- 30–50 thousand – for legal entities;
- 1–5 thousand – for entrepreneurs operating without forming a legal entity.
For repetition of similar violations, the punishment increases:
- 20–30 thousand rubles or suspension from activities for 1–3 years – for officials;
- 10–30 thousand – for those who are not a legal entity;
- 30–50 thousand – for legal entities.
By filing a lawsuit against the employer, the employee has the right to claim unpaid compensation, underpayment, compensation for moral damage, and legal costs associated with the trial. An employee has the right to file a claim with the appropriate authorities to recover additional payment from the employer before the expiration of 3 months from the date of dismissal.
Video
 Compensation for unused vacation
Compensation for unused vacation
If a person is injured as a result of an accident at work, they are entitled to compensation. JOB.RU expert, lawyer Olga Sokolova will tell you how to get it.
In the event of an accident at work, you should not succumb to the employer’s persuasion and negotiate benefits without drawing up reports and other documents. In this situation, an employee injured in an accident loses the legislative support of the state in the event of complications or subsequent refusal of compensation by the employer. This is beneficial for the employer - after all, without filling out documents, he will not come under the close attention of labor inspectors.
1. Qualify the accident
Accidents are regulated by Article 227 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. You can count on compensation for all injuries and damages sustained at work during the working day – including during breaks and overtime. However, they do not have to be directly related to your work. For example, you may fall on the way from one office to another - this will also be considered an industrial accident.
You also have the right to expect compensation if the accident occurred on the way to and from work, during business trips and business trips.
The order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 160 “On determining the severity of health damage in industrial accidents” describes in detail which injuries in the workplace are considered mild and which are considered severe.
In short, the severity of the injury is determined by how serious the harm is to your health, what medical consequences this may have for you, and how much capacity you have lost.
Severe accidents include: shock, coma, blood loss of more than 20% of the total volume, acute organ failure, penetrating injuries, some fractures (cervical vertebrae, spine, skull, chest), brain contusion, radiation injuries (from 12 Gy) , damage to the main blood vessels, termination of pregnancy.
All other cases (concussion, simple fracture, muscle strain, etc.) are considered mild.
At the same time, regardless of the severity, cases that resulted in: bodily injuries, including those inflicted by another person, heat stroke, burns, frostbite, drowning, electric shock, lightning, radiation, bites and other bodily injuries are subject to investigation. caused by animals and insects, damage due to accidents.
2. We control accounting and investigation
The rules for investigating and recording accidents apply not only to employees collaborating with the employer on the basis of an employment contract. They also apply to trainees, prisoners, persons involved in performing socially useful work and eliminating the consequences of accidents and other participants in the employer’s production activities (Article 227 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, the employer undertakes all actions to investigate and record accidents, as well as to provide proper medical care to victims (Article 228 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In the event of an accident, the employer is obliged:
Immediately provide first aid and transport victims to a medical facility, if necessary;
prevent the possible development of an accident;
leave the scene of the accident “as it was” at the time of the accident until an investigation begins (if this does not endanger other employees);
if it is impossible to preserve the situation, draw up diagrams, take photographs or videotape);
immediately inform the regional state labor inspectorate, the prosecutor's office at the scene of the accident, the compulsory social insurance insurer, the relevant trade union body, and the victim's relatives about the accident. Also, if the accident occurred on a business trip, you should notify the organization that sent the victim on this business trip;
in case of acute poisoning, the employer must also inform the territorial office of the Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in his region.
The employer is obliged to take these actions immediately after the occurrence of an accident.
The investigation of injuries at work is legally assigned to state labor inspectors. It is regulated by articles 229 – 231 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. To register accidents, a report on an industrial accident must be drawn up in two copies for each victim. This is not a medical report, but a detailed description of what happened, if necessary, with the attachment of photographic materials and testimony. Also attached to the acts is a medical report issued by the doctors who provided assistance to the victim. Upon completion of the investigation, the reports are signed by inspectors and certified by the signature of the head and the seal of the organization.
3. We issue a benefit
All employees are subject to compulsory social insurance and this is the responsibility of the employer (Article 6 of the Federal Law “On the Basics of Compulsory Social Insurance”).
If the victim works part-time in several organizations, he has the right to demand compensation from all places of work. This is explained in the letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation N3311-LG “On the procedure for assigning and paying benefits in connection with an industrial accident or occupational disease.”
To claim temporary disability benefits, you must provide the Social Insurance Fund with a copy of the accident report.
Compensation benefits are paid to the victim for the entire period of illness. In this case, the amount of the benefit is calculated in accordance with the length of service of the victim (Article 7 of the Federal Law “On the provision of benefits ...”). A benefit of 100% of average earnings (calculated for 12 months) is due to an employee with more than 8 years of experience, 80% to an employee with 5-8 years of experience, and 60% to an employee who has not worked for five years.