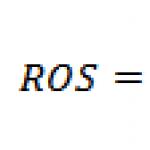Retail Report. What is the retail sales report document used for? Moving goods to a retail warehouse
Let's consider what capabilities the 1C Trade Management 11 program provides to its users for analyzing sales results.
UPDATE: added video “Sales analysis reports in 1C Trade Management 10.3”
From this video you will learn:
- How to analyze sales?
- How to build a sales report?
- How to view sales and balances in one report?
- How to build sales charts?
- How to view sales by payment?
Sales reports
By command "sales reports" We go to the sales reporting panel.
Similar articles:
- Tracking the movement of inventory balances in warehouses and...
- Formation assortment matrix and her...
The availability of reports in this panel is determined by whether the user has the appropriate rights to these reports, as well as by setting the visibility. Roles and rights are assigned to the user by the 1C program administrator. The user can control visibility himself using the command "Settings". In this case, checkboxes become available next to the panels; by checking and unchecking them, you can add or remove reports from this panel.
"Standard Terms of Sale"
Let's consider what opportunities we have for analyzing sales results. The first report is the “Standard Terms of Sales”. This report provides a list standard conditions sales, standard customer agreements registered in the system, and the basic information available in these agreements. Namely: name of the agreement; currency; type of price used; validity; our organization on behalf of which this agreement was concluded; business transaction (for example, sale or transfer to commission); taxation; stock; delivery time.
Price analysis
The next report is a price analysis. Available to us from documents such as commercial proposals, sales documents and customer orders. From each of these documents you can generate a report "price analysis". This report shows us information about the prices specified in the document (without a discount, with a discount), as well as about the prices of suppliers. Using this report, you can quickly analyze what prices we give to our customers and how they compare with the prices of our suppliers.
“Assessment of profitability of sales”
The following reports are also available from Sales Order documents. Namely, by opening the corresponding order, we can additionally display several reports in relation to this order.
The first of them is “Assessment of profitability of sales”. This report calculates the profitability of the order as a whole (including discounts, without discounts), and also provides detailed information for each item sold in this report. Now this report displays information about profitability of 100%. This is due to the fact that I have not yet calculated the cost price in my program for the current month, the routine closing operations of the period have not been carried out, and information on the cost price is not available. Accordingly, all proceeds are considered gross profit.
"Document Execution Status"
The following report is also available from the “sales order” ¾ this is the “Document Execution Status”. This report, firstly, provides information about the client’s debt (that is, how far the payment stages have been completed - say, advance, prepayment), information on shipment. And in the lower tabular part, in each product item, information is provided about what goods were shipped, in what quantity, for what amount.
Reasons for canceling orders
IN "Sales reports" There is a report on the reasons for canceling orders. This report collects information about the reasons why the order was canceled and provides quantitative indicators for each reason in terms of row cancellations in absolute and percentage terms. The information is also grouped by managers and by product price groups.
"Statement of settlements with clients"
The next report is “Statement of settlements with clients.” This report contains information on the status of mutual settlements with our clients. A list of our organizations and a list of clients is provided. The currency of mutual settlements is indicated. The counterparty on the part of our client is indicated. Information is provided on the debt at the beginning of the selected, analyzed period, information on the increase or decrease in debt, as well as the final balance and total balance.
"Customer debt"
The next report is “Client Debt”. This report shows information about customer debt. The information is grouped by debt currency. Information is provided about the client’s debt, our debt, settlement balances, as well as, based on information from the client’s orders, data on planned receipts from the client, planned sales to the client, or planned return Money at the client.
“Dynamics of overdue debts of clients”
The next report is “Dynamics of overdue debts of clients”. This report shows information about the growth rate of overdue debt. In the tabular section, information is grouped by clients and managers. In our 1C Trade Management program (UT 11) 11.2, currently no overdue debt is registered (all debt is current), so this report is empty and does not contain any information.
Client payment discipline
A report on the client’s payment discipline can also be used for analysis. This report groups data by customer, provides data for the period on the number of sales orders, how many of them are overdue, what is the percentage of overdue debt and the average period of overdue, and also data at the end of the selected period.
"Customer debt by maturity"
The next report that may be useful in the analysis is “Customer debt by maturity”. This report must indicate the date on which the information will be analyzed, as well as the classification of the debt. We currently have one classification in the program. Each created classification indicates the periods for which the debt will be analyzed for overdue. The main postulate here is this: the most recent statements are the easiest to collect. The longer the period of delay, the more difficult it is to collect the debt. In this report, we receive information about each client, the status of mutual settlements with him, as well as information about the period of overdue debt.
Payment card with counterparty
From "Customer's order" You can get a report on the settlement card with the counterparty. This report displays information about mutual settlements for the entire period, that is, on what documents were carried out monetary transactions, commodity sales or return operations. The total debt and information about its overdue status are also provided, if such data exists.
All these reports are available to us either in the section "Sales" in Group "Sales reports", or from settlement documents– documents used to document sales to a client, such as "customer orders" And « commercial offers clients".
Such opportunities are provided to us by the 1C Trade Management program version 11.2 for analyzing sales results.

Creating a sales report by manufacturer and revenue 1C UT 8.3
This video tutorial describes how to build a report on sales by manufacturer and the revenue received from them in 1C trade management 8.3. The main point of the report is from which manufacturers’ products we receive the most income.
Retail sales analysis
To analyze the sale of goods by retail outlets, quite a lot of reports have been implemented in the configuration.
All of them are available in the section Sales.
Conduct assessment of goods balances in retail outlets according to the selected price type, it is possible using a report List of goods of the organization in item prices. In the report, we can set the selection by store and by the type of price that is assigned to the store. We also determine the reporting period.

This report reflects the Beginning and Final Balance, Income and Expense, for each item.
We can customize this report in more detail. For example, we are only interested in information on the Coffee nomenclature and specific dates for the movement of this product.
To do this we go to Settings and on the bookmark Selections select the desired product.

As a result, the report we needed was generated. From the report we see that at the beginning there was no balance in the Maxi Store, on 06/27/2016 there was a receipt of 100 units, and on 06/29/16 there was a sale of two units. Total at the end of the period the balance of coffee is 98 pieces.

For control of funds at the KKM cash desk use the report Cash in KKM cash desks.

In the generated report, we see the Beginning and Final Balance, the Amount of Sales and Receipts of DS, as well as the withdrawal of DS by day.
We can generate this report with details on documents; to do this, in the report settings, set the checkbox to the value - Registrar. As a result, a report will be generated in the context of documents (registrars).

If the ending balance is minus sign, then the store did not fully account for the goods sold.
If the balance at the end of the period positive, then the retail outlet did not fully pay for the goods sold.
If we are only interested in information about the amounts received from the company’s cash desk, then in the advanced report settings, on the Fields and Sorting tab, we clear all unnecessary checkboxes; only the checkbox for the value Entering DS remains selected.

As a result, a report of the following type will be generated.

The program has the ability to generate a report in a regulated form Bargaining-29. This report is designed to analyze retail sales. The report reflects balances at the beginning and end of the month, as well as documents used to document the movement of goods through the specified warehouse and the specified organization. The total indicators in the report are calculated according to the price type specified in the card of this warehouse.
Prices are filled in according to the values that are valid on the report date.

Analysis of demand for goods
To analyze the demand for goods, you can use ABC and XYZ sales analysis. ABC analysis is possible based on several indicators. ABC analysis of sales by sales volume allows you to distribute goods into ABC classes in terms of demand for goods by customers. Class A will include the most in-demand goods, and class C will include the least in-demand.
Conducting an XYZ sales analysis allows you to determine the stability of product sales. From the point of view of sales of goods, XYZ analysis allows us to divide goods into the following classes - stable demand for goods, trends towards increasing demand for goods, one-time purchases (irregular consumption).
Carrying out a combined ABC and XYZ analysis will make it possible to determine the optimal control method inventory (that is, plan to purchase only those goods that are consistently purchased in total volume).
The program supports several inventory management methods: volume scheduling based on demand forecast, " order by reorder point"(with a fixed volume or with a regular delivery interval), " made to order". Different replenishment methods can be assigned individually to each product in each warehouse. The inventory management method can be determined automatically based on ABC/XYZ classification of reserves. It is also possible to manually change the inventory management method.

Example. In accordance with the conducted ABC/XYZ classification of reserves goods are classified as group AX (goods are sold stably and have a high turnover, that is, they bring trading company high income). For such goods, a method is established "Scope and calendar planning". Method "Order to order" is established for goods that belong to group AZ. For such goods, no stock is kept in the warehouse; the goods are ordered from the supplier only when a customer need arises (placing a customer order). Information about the presence of such goods in the warehouse is recorded in the report as excess stock and marked in red.
When analyzing the demand for goods, product restrictions (regulatory, minimum, insurance, maximum stock) are used. Product restrictions are calculated automatically using a regulatory task for each product item in each warehouse based on data on sales of goods.

When calculating the required (standard stock), the expected sales volume of goods is taken into account ( minimum stock) and possible surges in sales (safety stock). For additional insurance against the risk of shortage of goods, you can manually set a parameter such as the maximum stock of goods.
Filling out a sales plan using a formula
The video will help you navigate the types of needs, as well as understand why enterprises distinguish between these types.
Formation of orders according to plans
For some products, supplier lead times are very long, and it is impossible to order supplier goods to meet current needs - orders must be placed in advance. For such goods, it is proposed to form long-term purchasing plans and form orders to suppliers based on these plans.
Documentation procurement plan in the program can be formed both manually and automatically, based on various data sources from the program itself. As sources for the forecast, you can use: data from customer orders, sales volume for past period time, volume of purchases for a certain period of time, etc. You can also take into account the internal needs of the enterprise (orders from your own departments, orders from retail outlets, own stores, the need for components for assembly, etc.). In this case, it is possible to add several sources, as well as select the maximum value from all sources.

For example, you can select the maximum value based on sales volume for previous month and all issued orders for the supply of goods and internal orders for the same period or a similar period of the previous year.
The list of planning data sources can be filled in as desired. Templates are used to fill out.
Orders to suppliers are formed in accordance with the drawn up plan, and the deviation of the planned and actually ordered quantities from the supplier is controlled. Thus, purchasing plans can also be used to verify the implementation of plans dictated by the supplier itself.

Monitoring sales indicators
IN "1C: Trade Management 8" there is a mechanism that allows you to promptly identify “problem” areas and can help you take the right ones management decisions, and, in addition, automatically inform about situations when the state of indicators is still acceptable, but is already approaching critical.
So-called "Target Monitor" allows you to analyze key indicators the work of the department and the enterprise as a whole and the degree of achievement of the set goals, taking into account the target trend (increase in the indicator, decrease in the indicator, maintaining the indicator in a certain range). Information can be available to a manager anywhere in the world by accessing the “Target Indicators Monitor” functionality via the Internet.
In order for this to work, it is necessary to define the goals that are planned to be achieved. Each goal can consist of many subgoals, the successful achievement of which ensures the achievement of the fundamental goal.
Each goal is given a target indicator. In turn, for each target indicator, the target trend is indicated - the desired direction of changes in the indicator over time (minimization, maximization of the value or keeping within the acceptable value), and analysis options are configured.
For example:
The fundamental goal is revenue growth. This goal is planned to be achieved by increasing the number of customers and increasing the average sales amount. In turn, an increase in the number of clients is planned by attracting new clients and reducing the number of lost clients. And the increase in the average sales amount is planned by reducing the provided manual discounts.

Reflection in retail sales accounting is one of the most common transactions in trade. Retail sales in 1C 8.3 Accounting are accounted for using a special document - a report on retail sales. Filling out this report can be automated, or you can generate it manually. Read this article on how to fill out a retail sales report in 1C 8.3.
For an accountant every dayWhen selling goods at retail, several transactions must be reflected in accounting:
- Receipt of funds from the buyer (cash or non-cash);
- Reflection of revenue on the credit of account 90;
- Write-off of cost of goods sold.
In 1C 8.3 Accounting there is a special document that forms these operations - a retail sales report. There are two ways to create it:
- In automated mode
- In manual mode
If the store has equipment and software that records everything online goods movement, then such a point of sale is considered automated. In this case, using special 1C software, you can automatically generate a report on retail sales in 1C 8.3.
If the store does not have equipment for detailed accounting of sales, then such a retail outlet is considered non-automated. The report on retail sales in such cases is done manually or based on inventory. As a rule, non-automated points are trays, kiosks and small shops.
In 1C 8.3 Accounting in the “Warehouse” directory for each point of sale you need to choose one of two types of warehouses:
- Retail store;
- Manual point of sale.
For stores with automated accounting, choose the first type of warehouse. For other points of sale, select the value “Manual point of sale”.
How to make the necessary settings in 1C 8.3 Accounting in a few steps and fill out a report on retail sales, read in this article.
Quick transfer of accounting to BukhSoftStep 1. Set up 1C 8.3 Accounting for retail trade
To account for retail in 1C 8.3 Accounting, you need to make some settings. To do this, go to the “Administration” section (1) and click on the “Functionality” link (2).
In the window that opens, go to the “Trade” tab (3) and check the box next to “Retail” (4). If necessary, also check the boxes next to the words “Gift Certificates” (5) and “ Alcohol products"(6). Now the 1C 8.3 Accounting program is ready for retail accounting.

In retail, there are two ways to account for product valuation:
- By purchase price;
- At sales price, using account 42 “Trade margin”.
It is necessary to establish one of the methods in the accounting policy of the organization. To do this, go to the “Main” section (7) and click on the “Accounting Policy” link (8).

In the window that opens, indicate your organization (9) and select one of the assessment methods:
- “At acquisition cost” (10);
- “At sale price” (11).

The necessary settings have been made, and you can begin recording retail transactions.
Step 2. Create a report for a manual point of sale manually
If your store is not equipped automated system accounting for sales, then you can generate a report on retail sales in 1C 8.3 Accounting manually. To do this, go to the “Sales” section (1) and click on the “Retail Sales Reports” link (2).

In the window that opens, you see a list of previously created documents. Click the “Report” button (3) and select the “Manual point of sale” link (4). A form for creating a document will open.

In the window that opens, specify:
- Formation date (5). If the report is generated over several days, put the last date of the period;
- Your organization (6);
- Warehouse (Retail outlet) (7). A separate warehouse is created for each point. We remind you that the warehouse type in in this case must be “Manual point of sale”;
- DDS article (8). Select the value “Retail revenue” from the directory.
In the product section, fill in:
- Sold item (9);
- Its quantity (10);
- Selling price (11);
- VAT rate (12).
To conduct, click the “Post and close” button (13). The document will be posted only if cash receipt orders or payment card transactions are created during the reporting period. Moreover, the amount in the report must match the amount of payments at the cash register and card transactions. If the amount of payments for the reporting period is 140,000-00 rubles, and the amount of goods sold in the sales report is 145,000-00 rubles, then when posting the document there will be an error message: “Available retail revenue for sales: 140,000, required: 145,000. Missing The proceeds must first be capitalized using the Cash Receipt document.”

The document has now appeared in general list reports. When it is carried out in accounting 1C 8.3 Accounting, entries are generated to write off the cost of goods sold. Also, postings are created on the off-balance sheet accounts of RV “Retail Revenue” and postings for adjusting revenue in account 90 “Revenue” (entries for the total amount are reversed and new ones are generated, broken down by item and quantity).
Step 3: Create an Inventory Report
A report on sales at a manual point of sale can be created from an inventory document. This document automatically calculates the accounting quantity of goods on the inventory date. It also manually indicates the actual quantity of goods identified as a result of the recalculation. The difference between the accounting and actual quantities of goods will be transferred to the retail sales report. Next, read how to create such a report in 1C 8.3 Accounting.
Create an inventory of goods in 1C 8.3
Go to the “Warehouse” section (1) and click on the “Goods Inventory” link (2). A window with previously created inventories will open.

In the window that opens, click the “Create” button (3). The inventory form will open.

In the “Product Inventory” window, specify:
- Inventory date (4);
- Your organization (5);
- Retail outlet (warehouse) (6);
- Responsible person (7).

Now in the product section in the “Accounting quantity” field (10) we see the balances according to the data accounting. In the “Actual quantity” field (11), manually enter the actual quantity of goods as of the inventory date. After this, the quantity of goods sold will be automatically calculated in the “Deviation” field (12). To carry out an inventory, click the “Record” (13) and “Conduct” (14) buttons.

Generate Retail Sales Report from Product Inventory
To create a sales report, click the “Create based on” button (15) and select the “Retail sales report” link (16). The completed sales document will open.

In the document that opens, indicate the correct date (17), check the quantity sold (18) and the selling price of the goods (19). To reflect sales in accounting, click the “Post and close” button (20). Now in accounting there are entries for writing off the cost of goods sold. Also, entries were generated on the off-balance sheet accounts of RV “Retail Revenue” and entries for adjusting revenue in account 90 “Revenue”.

Step 4: Create a retail sales report for the automated point of sale
If your store is equipped with an automated sales accounting system, then a retail sales report in 1C 8.3 Accounting is generated automatically. To see it, go to the “Sales” section (1) and click on the “Retail Sales Reports” link (2). A list of previously created documents will open.

There are two types of reports in the list:
- With the type of operation "Retail store";
- With the type of operation “Manual point of sale”.
In reports on an automated point of sale, the type of operation should be “Retail store” (3). This report, as we have already said, is automatically loaded into 1C 8.3 Accounting. The loading schedule depends on software your store. Before running the report, go into it and check all the data. To enter it, double-click on it in the general list of reports (4).

In the report that opens, check the date (5), point of sale (warehouse) (6), quantity (7) and sale price (8) sold goods. At the bottom of the window, check the total amount (9) with the amount of payment received for the reporting period. These two indicators should be equal. After checking, check the document. To do this, click the “Post and close” button (10). Now, accounting entries have been created for writing off the cost of goods sold and for recording revenue. Also, the report on retail sales for an automated point of sale generates transactions for receipt of cash payments. This differs from a report on a manual point of sale, where payment transactions are generated by receipts.

A report on an automated point of sale can also be created manually, similar to a report on a manual point of sale.
Attention - this is important! As we have already said, the report on retail sales at an automated point itself generates transactions for the receipt of cash payments. In order for these payments to be reflected in cash book you need to create a cash receipt order. In order not to double the entries for the receipt of money in accounting, in the cash receipt order in the “Type of transaction” field, you must indicate “Retail revenue”. In this case, the parishioner will not form accounting entries, but will be reflected in the cash book.
The document "Retail Sales Report" is intended to reflect sales in retail trade.
"Report on retail sales" can be entered on the basis of the document "Inventory of goods in warehouse", "Reflection of sales simultaneously with the receipt of retail revenue" (warehouse type "Wholesale" or "Retail"), "Reflection of sales based on previously accepted revenue" (warehouse with view "Manual point of sale").
To reflect retail sales from a wholesale warehouse or warehouse with the "Retail" view in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, follow these steps (Fig. 1):
- Menu: Sales – Sales–Retail sales reports.
- Click the "Report" button, then select "Retail store" or "Manual point of sale". If an organization carries out retail sales through an automated point of sale, then the funds technical support or the specifics of trading activities make it possible to generate a daily detailed report on goods sold for subsequent entry into an information base, for example, into the 1C: Accounting 8 program. If you select the transaction type of the document “Manual point of sale”, then the organization’s point of sale is considered manual, since daily registration of goods sold is not maintained there. Information on goods sold at a manual point of sale may be received with some delay based on inventory. In this case, the number of goods sold for each item is determined as the difference between the accounting data from the information base and the data obtained by inventory. In the case of keeping records in sales prices, it is possible to obtain information about goods sold only in total terms, without a detailed breakdown by item.
- Fill out the required document tabs that reflect the relevant sales or form of payment. The “Products” tab indicates the goods and services sold to the retail buyer. In this case, the fields “Price”, “Amount”, “% VAT”, “VAT”, “Total” will be filled in automatically based on retail prices and the specified quantity that need to be checked.
- In the "Accounting account" field, select account 41.11 "Goods in retail trade (in ATT at sales price)", if goods are accounted for at sales prices and using an automated point of sale. The choice of account depends on the accounting policy settings (Fig. 2).
- To call up the printed form "Cashier-operator's certificate-report" using the KM-6 form, you can use the "Cashier-operator's certificate-report (KM-6)" button.
This lesson shows how to maintain retail sales for three types of cash register cash registers, cash flow and the formation of sales analytics.
First, let's look at retail sales in the easiest version, using an autonomous cash register.
Autonomous cash register
In this situation, the cash register is not registered in UT 11 in any way; primary sales accounting is carried out in a notebook/Excel.
You will need to independently create a document Retail Sales Report and reflect the sales data for the day in it:
In the list of documents, select our cash register with the Autonomous cash register type:


We create a new document, on the first tab we indicate the sold goods:

On the second tab we indicate the amount paid by customers using a bank card:

The following tabs provide information about gift certificates and bonus points (we will discuss this in detail in the following lessons):

The following printable forms can be printed from the document:

That's all, sales in the offline checkout have been successfully reflected.
Fiscal registrar
To record sales at the cash register of a cash register with the Fiscal Registrar type, there is a separate workplace cashier (RMK):



The cashier's workplace looks like this:

Because We have accounting enabled in the settings personal sales managers trading floor, for each sale, not only a cashier, but also a seller must be selected:

After selecting a vendor, the workspace title changes. Now we can select goods for the receipt (using a scanner or manually through the selection form):

IN standard form selection we choose necessary goods and transfer it to the document:

We encountered a problem - the price was not entered:

The reason for this is that a price type was selected in the warehouse card for which item prices were not set:

Let's select the correct type of prices, now the prices have been successfully filled. But another potential problem is visible - there is no button for paying by bank card:

In order for it to appear in the RMK settings, let’s add an acquiring terminal:

Now the button has appeared, click the payment button:

The program warns that the cash register shift is not open (every morning you need to start with the opening of the shift), we agree:

Enter the received amount of cash:

Now I’ll demonstrate payment by card, create a new receipt:

I fill in the goods, click payment by card:

The program asks whether the card payment went through on the terminal itself:

If it passes, then we punch the check:

If necessary, in addition cash receipt We can print the product brochure:


If the client delayed payment for some reason, we can postpone the check (in this case, the goods can be reserved for the client, or not reserved):

Then, when the client returns with the money, you can return to the deferred check:

The program immediately shows what pending checks are available:

Now we can accept payment by check:

After closing the store must be closed cash register shift(take a blanking report, Z-report):

As a result, a z-report is printed on the fiscal registrar, and a retail sales report is automatically created:

In addition to filling in the goods sold, information about the amounts paid for acquiring is filled in:

To analyze retail sales, there are the following reports:






Now let’s withdraw funds from the cash register cash register:

Enter the amount:

Now all that remains is to issue a cash receipt order (for posting the DS to the organization’s cash desk):



In the statement of funds we see that the movement of cash flows is reflected correctly:

Now, as an example, let’s reflect the deposit of money into the cash register cash register from the organization’s cash desk. To do this, we will create an expense cash order:



Please note that the button Application in RMK you do not need to press:

KKM offline
Now let's look at working with the third type of cash register cash registers - cash register offline. The principle here is the following - first, analytics on goods and prices are downloaded from 1C into an XML file of a special format. Then this file is uploaded to the cash register and all sales are processed at the cash register itself. At the end of the day, the shift closes at the cash register and as a result, an XML file with sales data is generated on the cash register. Then this file is uploaded to 1C and as a result a document is automatically generated Retail sales report.
Let's open an exchange workplace with a cash register:

Let’s create a rule for uploading information about products:

Upload to cash machine We will only use goods that are left in stock and for which the price has been set:

Now we upload the goods to a file:

We get a file of this format:


If desired, you can set up automatic file exchange between 1C and the cash register at an arbitrary time interval:

Let me remind you that in order for the cash register itself to be available in the exchange workplace with the cash register offline, it must be selected in the settings of the current location:

In the 1C: Accounting 8 program, starting with edition 1.6, it became possible to reflect calculations with retail buyers not only when paying in cash, but also when paying with payment cards and using a bank loan. This article, prepared by 1C methodologists, examines the procedure for reflecting non-cash payments in retail in the program using the example of customer payments with plastic cards.
Retail sales report
Retail sales in the 1C: Accounting 8 program are reflected in the document “Retail Sales Report”.
In the report on retail sales of cash register machines of the trading floor for a certain date, on the “Products” tab, you should indicate the product composition, quantity, price and amount of goods sold per day.
If, in addition to cash payments, payments were made with payment cards during the day, you must fill out the “Payment cards and bank loans” tab. The payment type is selected from the directory of the same name, the elements of which contain the following data:
- payment type - payment card or bank loan;
- organization - a sales organization that prepares a report on retail sales;
- counterparty (for payment cards) - a bank with which an acquiring agreement has been concluded for servicing plastic card holders;
- counterparty agreement (for payment cards) - acquiring agreement for servicing plastic card holders;
- settlement account - settlement account with the bank under the acquiring agreement;
- % bank commission - the percentage charged by the bank as a commission under the acquiring agreement.
When conducting a report on retail sales, the corresponding transactions are generated.
If there are several payment options, the revenue is reflected in the intermediate account 62.Р “Settlements with retail customers”, after which it is distributed according to payment methods.
Registration of cash receipt order
Based on the retail sales report, a cash receipt order is generated for the amount of cash payment. It does not generate transactions, since transactions for the receipt of money in the cash register are already generated by the retail sales report.
Receipts from sales with payment by payment cards
Receipt of funds from sales with payment by payment cards is reflected in the documents “Incoming payment order” with the transaction type “Receipt from sales of payment cards and bank loans”.
Additionally, on the “Accounting for Bank Services” tab, information about the bank’s commission is indicated.
When posting a document, the corresponding postings are generated.
If the transfer of funds is executed without issuing a payment order, for example, with a memorial order, instead of the document “Incoming payment order”, you should use the document “Payment order for receipt of funds” with the same type of transaction.