Project implementation schedule. Practice of drawing up a project schedule in MS Project Plan project implementation schedule sample
When planning the implementation of any task, the traditional questions are: “What to do?”, “When?”, “Who?”, “What are the results?” And since a project event includes a whole set of actions, the group of documents of the master plan must necessarily contain a project schedule, which is also called a project schedule or calendar plan. In this article we will look at the preparation steps and options for visual presentation of this document.
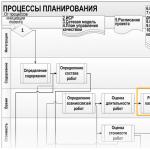
Reflection of the project content in the schedule
We discussed the stages of developing a calendar plan in the material dedicated to. The quality of creating a schedule depends on the manager’s fulfillment of a number of mandatory procedures, among which taking into account the main restrictions (on content, time and resources) occupies a central place. The first step on this path is planning the content of the project as a certain set of services and products on the subject of the task. The content of the project is a fairly capacious concept that includes:
- a descriptive part justifying the reasons for launching the event, as well as the opportunities it brings;
- goals and results of tasks at different levels of decomposition of the main result-product;
- identified connections between the project and the company’s development strategy;
- a variety of approaches to solving a unique design problem;
- the project boundaries within which the PM's product, authority, and responsibilities arise;
- event product;
- basic requirements for the product and its parameters;
- all kinds of assumptions and assumptions regarding the conditions of the project;
- identified limitations;
- performance criteria.
In this list, we will be interested, first of all, in planning the scope of work, for each of which results are established, responsible resources for the corresponding tasks and deadlines. In other words, the entire sequence of tasks translated into the format of work leading to the result of the project must be summarized in a table or graph of a certain form, including the named parameters of the task nature.
You and I know from the articles on our site that tasks are the essence of results as certain points in the future in the interpretation: achieved or not achieved. For tasks, the moment at which actions begin is not important, but the timing of their final solution is important. Tasks are a static category, but we transfer them to a dynamic state of work, i.e. actions that have a beginning, an end, responsible persons and results. Let us recall the visual image of the procedural model of planning execution and determine the place in it of the development of the calendar plan.

The conditions for the implementation of the project are dictated by the content, the defined scope of work, the identified relationships between them, and the established duration of the operations. But that's not all. Management at the time of implementation of the schedule is carried out taking into account the identified, assessed risk and the developed project budget. Among the group of substantive processes for developing a calendar schedule, in addition to the composition of work, a number of other parameters are also important.
Clarification of work parameters
Determining the scope of work is carried out in order to obtain information about the entire range of works for the project. A set of complete data on the composition of planned operations is produced. Planning the structure and scope of work for a project is related to its goals. It is based on the goals and the tasks arising from them that the team leader determines the required scope of work and sequence of actions.
In this he is helped by the decomposition method, which cannot be called simple. The manager has to tune in in a special way, be disciplined, focused on the rules and criteria of division. As a result, an intermediate document appears - the WBS (an example of the hierarchical structure of work is given below).

Example of a functional partition type WBS
The next parameter of the work is the level of their interrelations. It also needs to be determined before the project schedule is formed. Planning work relationships has the goal of establishing, coordinating and documenting the sequence of operations. To accomplish this task, logical and mathematical algorithms are used to construct a network model of the project. In this case, mutual connections are taken into account not only between activities, but also between milestones. Other restrictions are also taken into account. The network diagram uses:
- special types of relationships between operations;
- critical path method;
- methods for calculating the duration of operations;
- network diagram optimization management.
Another parameter that precedes scheduling is the duration of the work. Solving the problem of the duration of operations serves as a clear understanding for the manager of what will make up the total duration of the investment event. Management of this temporary resource is subsequently based on the initial inventory of projected events and actions. Moreover, as we know, there can be an infinite number of models for solving any unique problem. It all depends on the creative message and past experience of the responsible resource, his ability to critically evaluate alternatives for achieving results and the associated risks. The key criteria, in addition to composition, sequence and relationships, are:
- duration of work;
- labor costs for performing operations.
Estimating duration and labor costs are also the responsibility of the PM. But under the conditions of task decomposition, the project manager as a director also has responsible resources in the form of team members and external contractors. Expert consultants are also involved in local decisions and bear slightly different responsibilities for the proposals and recommendations they put forward. Together, these participants must provide an estimate of the duration of the work and the required composition of labor resources. For the purposes of this article, we do not take into account a number of additional planning aspects. This refers to planning and assessing the cost of work, risk, and quality planning. They influence the project schedule indirectly, although they are no less important for the master plan than everything else.
The actual calendar plan
The project implementation schedule is developed with the aim of finalizing the estimated timing of the operations included in its composition and the total duration. In this case, final agreement with the participants and approval of the schedule document must be ensured. It is the operational mode of application of this document that determines the significance of its approval. The level of detail in the schedule should be sufficient, but not excessive. What does this mean?
A universal criterion for the depth of schedule development is the presence of a responsible resource for the result of a task allocated for independent work. If the person responsible for related operations remains the same, there is no point in further dividing the higher-level work. But if the results of actions from one responsible person are transferred to another, then the process of dividing the work is not yet completed.
If all previous documents (milestone plans, WBS, network models, etc.) were of a preparatory nature, then the calendar plan is a direct document of execution and control. It is not for nothing that plan-fact analysis, monitoring and control of the progress of work are carried out on a regular basis precisely on the basis of the schedule. The schedule performs a number of functions:
- an administrative document prescribing the implementation of specific actions;
- monitoring resource;
- document for control activities;
- document-basis for making a decision to change project plans.

Above is an example of a project schedule made in the standard Microsoft Project application, which has a dual view: tables and Gantt charts. Work progress can be managed based on schedules of various visual representations. Among these types, the following stand out.
- Tabular form.
- Strip chart.
- Gantt (or Gantt) chart.
- Diagram of milestones (graph by milestones).
- Network diagram taking into account the time scale.
Finally, we will look at another example of a schedule in the form of a table. This is the most common and working type of schedule design. The tabular form includes the main parameters of the work: content of operations, start and end dates, responsible persons, expected results, completion mark. Project planning management does not end with the schedule. There are several iterations of adjusting the budget and the schedule dependent on it. An organizational structure is developed, risks are assessed, deliveries and quality are planned. And only after this the plan is compiled into a consolidated document.

Example of a tabular form of a project schedule
In this article, we examined the issue of preparing a project schedule and its place in the overall system of planning processes. In small projects, it happens that the entire planning complex is limited only by the schedule and budget, but if the event is large-scale and significant, the algorithm becomes expanded into a number of successive stages. A project manager who is skilled in this work and is not afraid to experiment with ways to solve problems almost always finds options when the limitations are leveled and the expected result of the team’s actions occurs on time.
A network diagram is a dynamic project model that reflects the sequence and dependency of the activities required to successfully complete the project. The network schedule reflects the timing of the planned work and the resources required for their implementation, as well as direct financial costs arising from the implementation of these works.
In English for definition network graphics term used Project Network — is a graph depicting the sequence in which a project’s terminal elements are to be completed by showing terminal elements and their dependencies.
The main purpose of using a network diagram is effective planning and management work and project resources. At the same time, resources in this context mean both equipment, production capacity or money, as well as labor resources, internal or external to the organization carrying out the project.
The greatest efficiency of using a network diagram is achieved when it is used to plan projects or individual interrelated works. The network schedule allows you to quite accurately determine the planned completion dates of the project and identify possible options for reducing them. And, more importantly, the network diagram allows you to identify . In addition, the network schedule allows for basic control over the progress of the project, its timing and budget execution.
Types of network graphs
A network graph is a graph in which events (states of activities or objects at a certain point in time) are represented as vertices, and project activities are represented as arcs connecting the vertices of the graph. The network diagram presented in this form is initially part of the method.
In practice, another version of the network diagram is more often used, when the vertices of the graph are jobs, and the arcs indicate the relationship between them. This type of network diagram is part of ( English, CPM - Critical Path Method).
Let's consider the second version of the graph and the algorithm for constructing it in more detail.
Algorithm for constructing a network diagram
The algorithm for constructing a network diagram using the critical path method consists of the following 10 steps.
Determine the main goal of the project - the result that should be obtained after the successful completion of the project. This is necessary to define the boundaries of the project and an initial estimate of its time frame.
Step 2: Identify Limitations
Identify constraints affecting individual project activities or the entire network schedule. Typical constraints are resource availability, timing, or cost. In addition, restrictions may be set by legal requirements.
Determine the scope of work necessary to achieve the goal set for step 1.
Estimate duration each of the tasks and determine the resources necessary for its successful completion. The project management team should agree on what units of measurement to use to estimate the duration of activities (hours, days, or months, for example), and also develop requirements for the maximum duration of one activity. All work exceeding this duration must be.
Determine the sequence of work. Determine the work that needs to be done first. In some cases, there may be several such works and they will be performed in parallel. This job should be the leftmost one on the graph.
Determine the work that must be completed immediately after the first one. Next, the job is determined that should begin immediately after the second, and so on until all jobs have been considered. If work begins before the previous one is completed, then the previous work must be divided into components. Work can be performed in parallel, but provided that the connection between the work is clearly defined.
The start of parallel work must be strictly tied to the completion of previous work.
Indicate connections between jobs, usually in the form of arrows that show the sequence of work. The direction of the arrows is set from left to right.
Determine early start and early finish for each of the works. To do this, the network diagram is viewed from left to right, starting with the first job (far left) and then moving in turn to the last one. Subsequent work cannot begin until all previous work has been completed. The early start of subsequent work will coincide with the early completion of the previous one.
If there are several preceding jobs, then the earliest start of the subsequent job will be the largest of the early finish values of one of the preceding jobs. The early finish of each activity is defined as the early start plus the duration of the activity, estimated at step 4.
Determine late start and finish for each of the works. To do this, the network diagram is viewed in the opposite direction - they start with the last work (the rightmost one) and then move to the first one in turn. The preceding activity must be completed before each subsequent activity begins. The late finish of a job will coincide with the late start of the subsequent job. If there are several subsequent jobs, then the late finish of the job will be the smallest of the late start values of subsequent jobs. The late start of each job is defined as the late finish minus the duration of the job.
Determine slack for each of the works. Slack is calculated as the difference between late and early starts or late and early finishes.
—uh then a chain of works for which the slack time is zero. When optimizing a network schedule, the first step is to optimize the work that lies on the critical path.
An example of constructing a network diagram
Although the algorithm described above may seem complicated, in fact, constructing a network diagram is not a difficult task. To make sure of this, let’s consider constructing a network diagram using a simple example of renovating a children’s room.
Step 1. Determine the main goal of the project
Imagine that it is summer, your son is 7 years old and he is going to school in September. You have decided to update his room for the new school year and make it suitable for a school student, i.e. a full-fledged workplace should appear, the zoning of the room should change, etc.
In this case, the goal of our small project will be − make the room suitable and pleasant for a boy who will go to primary school to live in.
Step 2: Identify Limitations
The budget is no more than 100,000 rubles, repair work can only be carried out on weekdays from 10:00 to 18:00 with a mandatory break from 12:00 to 14:00. The total is 6 working hours a day.
Step 3. Determine the scope of work
After some thought, we outlined the main work that needs to be done, namely:
- We need a design project for a new room;
- We need to purchase materials for repairs;
- It is necessary to draw up an estimate for repairs;
- It is necessary to carry out the repair itself;
- And because We decided to do a small redevelopment, then we need to coordinate it with the HOA.
Let's display these works in the form of blocks:

Figure 1. Scope of work
Step 4. Estimate the duration of the work
We decided to estimate the duration of work in days, because... There is still enough time before the start of the school year, so such precision in planning suits us quite well.

Figure 2. Duration of work
Step 5. Determine the sequence of work
Now we will determine the sequence of work; we will use a top-down network diagram. The first job that needs to be done is the work " Develop a design project". Then we will estimate the cost of the project, and at the same time we will begin coordination with the HOA, because this task takes a lot of time. After we evaluate the project and approve it, we will begin purchasing all the necessary materials and only then begin the repair itself.

Figure 3. Sequence of work
Step 6. Indicate connections between activities
We indicate with arrows the connections between the works.

Figure 4. Connections between jobs
Step 7: Determine Early Start and Early Finish
Because We have chosen a “top-down” network graph model, then we start and look through it from top to bottom, starting with the topmost work, and then move in turn to the lowest work.
Recall that the early start of a subsequent job will coincide with the early completion of the previous one, and the early finish of each of the jobs is defined as the early start plus the duration of the work. If there are several previous jobs, then the early start of the subsequent job will be the largest of the early finish values of one of the previous jobs.

Figure 5. Early start and finish of work
Step 8: Determine Late Start and Finish
In order to determine the late start and end, let's look at the network diagram in the opposite direction - from bottom to top. The late finish of a job will coincide with the late start of the subsequent job. If there are several subsequent jobs, then the late finish of the job will be the smallest of the late start values of subsequent jobs. The late start of each job is defined as the late finish minus the duration of the job.

Figure 6. Late start and finish of work
Step 9. Determine slack
Let's calculate the time reserve for each of the jobs. It is calculated as the difference between late and early starts or late and early finishes.

Figure 7. Time reserve
Step 10. Identify the critical path
As we already know, the critical path is a chain of activities for which the slack time is zero. Let us highlight such tasks on the network diagram.

Figure 8. Critical path
Tasks " Develop a design project«, « Coordinate the project with the HOA" And " Purchase the necessary materials«, « Carry out repair work“I make up the critical path, and its length is 19 days. This means that in its current form the project cannot be completed in less than 19 days. If we want to reduce the project timeline, then we need to optimize the tasks lying on the critical path.
For example, we can begin repair work before receiving approval for redevelopment from the HOA, taking on the risks that approval may not be obtained.
Views: 31,961
,
Planning is considered an important component of effective project management. The schedule, the main element of planning, visually represents the time frame for completion, sequence, degree of importance and other characteristics of work.
A well-designed calendar schedule allows you to effectively plan and implement a project due to the coordination of the actions of the performers and compliance with deadlines.
Main types calendar schedules
Depending on the scope and scale of projects, the following types of calendar schedules are distinguished:
- The summary table displays the order of project tasks, start and completion dates, and the duration of each stage.
- The object schedule shows the timing of each stage of the plan, broken down by days or months.
- The work schedule is prepared for a short period of time during the implementation of the project and is an element of operational management.
- Time schedules (hourly or minute) are usually prepared by technical map developers. Focused on standard external factors, such schedules require numerous amendments during project implementation.
Levels of calendar charts
When scheduling, a system of distributing schedules by level is used. Usually 4 levels of charts are used. (project manager)
Level 1 schedule:
The first level includes general, non-detailed project plans. Enlarged plans are developed first when starting a new project. Data for schedules is collected during negotiations with the customer; often he has his own key indicators for project dates, stages and final goals. By collecting this data, you can form a general roadmap. Only important key events are included in it. The roadmap is updated depending on the overall duration of the project; if the duration of your project is five years, then it is enough to update the first level schedule once a year. If there are many key milestones in the roadmap, then it is necessary to determine the update period so that at least one key event falls into it. The roadmap can be developed by both the Customer and the Contractor, but in general this responsibility lies with the Customer.
Calendar schedule2nd level:
After the project roadmap has been agreed upon and approved, the stage of detailing to certain stages begins. Basically, the second level schedule is an annex to the agreement between the Customer and the Contractor. The development of a second-level schedule is also the responsibility of the Customer, and is submitted to the Contractor for approval; often the stage schedule is developed by the Contractor based on its resource capabilities. In the second level plan, no special detail is needed; it is enough to follow the sequence of project implementation and generally determine the scope of work for the project. Updated along with the roadmap.
Calendar schedule3rd level:
After concluding the contract, the Contractor prepares a detailed work schedule for the project with a more detailed description of the work within the stage. Those. The general stages of the second level schedule are detailed by type of work. The duration of work is from 2 weeks to a month, depending on the total duration of the project. If the plan is less than a year, then the detailing ends there. Although everything depends on the agreements with the Customer.
Calendar schedule4th level
Designated as weekly-daily planning. Updating the plan every day, two days, a week, depending on control needs. The most labor-intensive, costly and accurate method of project control. The updated information from the fourth level graph rises up the hierarchy, and based on this information, all upper graphs are updated. Changes at this level can lead to recalculation of the entire plan and to re-coordination of implementation deadlines down to the roadmap.
The procedure for developing a calendar schedule
Creating a calendar schedule contains the following steps:
- Preparation of a detailed list of all necessary tasks for the project, determination of their volumes.
- Development of WBS, that is, a visual representation of the plan in the form of hierarchical interconnected blocks.
- Selection of methods and technologies used in the implementation of the plan. Calculation of the labor intensity of completing project tasks.
- Determining the composition of project teams. Development of a network diagram that clearly represents the sequence of execution of all tasks.
- Preparation of data on the duration and possibility of parallel work - development of a Gantt chart.
- Comparison of the estimated duration of work with the standard, making appropriate adjustments.
- Development of schedules for resource requirements (personnel, equipment, materials).
- Calculation of labor costs.
Typically, the project schedule is developed by the project manager, who, if necessary, consults with the experts involved.
Schedule preparation software
The use of special programs allows you to quickly respond to deviations that arise during the implementation of projects.
One of the most popular universal project scheduling tools is the Microsoft Project program. Using MS Project allows you to build a Gantt Chart, assign the required resources to tasks, determine the time frame for the project and its budget. A schedule made in Project visually displays the workload of staff with certain tasks.
The scheduling software product Primavera is used mainly in large-scale projects with increased complexity, in particular in the engineering and construction industries.
Planning is an integral component of project implementation. The key point in planning is the creation of a calendar plan or, as they sometimes say, a calendar schedule. A schedule plan helps you meet the requirements of project work and clearly understand what activities will be performed and for how long.
The article presents the parameters of the schedule, technologies and methods of creation, programs and project executors. A list of documents providing planning is provided.
To begin with, it is worth defining project scheduling. Scheduling is a combination of documented decisions that answer the questions: why, how, when and by whom the project will be implemented. The calendar plan is the result of planning, its material confirmation, presented in the form of a comprehensive diagram. The scheme is checked and approved by the company management.
When a calendar plan is created, mandatory and applied tasks are solved. During planning it is necessary:
- Clarify the purpose and target audience of the project. Understand the details.
- Explain details to the customer.
- with those involved in the project and with the customer.
- Determine the amount of work and its composition.
- Attract and rationally distribute resources, both human and material and technical.
- Create a budget.
- Assign responsibility for implementing the plan and divide responsibilities.
- Set deadlines for completing the project and individual plan items.
The schedule is presented either as a complex diagram or as a simple list of work and due dates.
For how the project is progressing, the project manager. He is also appointed as the manager according to the calendar plan. The manager is subordinate to performers who are responsible for individual items of the plan and provide reports on the work. If inconsistencies arise during work, the manager is obliged to find out their reasons and adjust the plan. To solve global planning problems, meetings are held at which the fate of individual stages and the entire project is decided.
All participants must be aware of the role they perform. They must be provided with the required documents, a workplace, high-quality tools and materials for carrying out activities.
Scheduling is used to organize activities and improve productivity. The plan helps you see an expanded and accurate project schedule.
Schedule Options
Main parameters of the calendar schedule:
- start and finish of work
- duration of work
- resource base

Start and finish of work. Early start – the official start of work. Late finish – the date on which the work is scheduled to be completed. In addition, there is an even later start and early finish. The period between the initial dates and the closing dates is called slack. Typically remains the same, so the slack between early and late starts and early and late finishes will be the same.
Duration of work. Depends on the number of performers and their labor costs, the volume of work, customer requirements and other factors. Critical duration is the minimum within which the bulk of the work or even the entire project must be completed.
If we add up early start/late start and duration of work, we get early finish/late finish.
Resources. Resource constraints are taken into account when project development dates are set. After identifying the needs for all types of project work, the required amount of resources for each of them is calculated. Based on this, a graph of resource levels is constructed, the data of which is compared with the existing amount of resources. If the needs exceed the resource base, then it is possible to change the time in the calendar in order to cover them.
Basics of Creating a Schedule
In order to implement a calendar plan, you need to understand the methods and technology of its creation, as well as study the tools for convenient planning.
Technology
The project is a single whole. For convenience, it is divided into interconnected large blocks. These blocks are then broken down into smaller units and steps to simplify the project. This approach helps activities and avoids mistakes that can be overlooked if you do not start working comprehensively and in detail.
Project implementation stages are related to work parameters and include:

- Compiling a list of works that need to be completed to implement the project.
- Calculation of duration, sequence of work and degree of project implementation.
- Identification of the availability of human, material, information and other resources.
- Identifying external constraints. They can be seasonal, resource-based, time-related, etc. The main limitation is the deadline for completing the project.
- Search for risks. There is a special formula for this: a risk (which is possible) may occur because (reason) it will lead to consequences.
- Developing a plan to respond to risks and threats. This is done through response strategies. There are two of them: passive and active. The first involves the creation of a cash reserve for identified risks, and the second is aimed at minimizing risks by including new work in the plan.
It is important to remember that the schedule is a model for project implementation, which is implemented gradually. Work on a new stage begins only when the implementation of the previous one is completed. This model is not completely static because planning can be adjusted and revised.
Methods
Various methods are used to create different types of plans or to develop individual parts of a plan. Here are the most popular:

- A Gantt chart is a bar graph created to illustrate a work schedule.
- A network diagram is a comprehensive model for displaying the sequence of work of a project.
- A volume-calendar schedule is a method that allows you to present the volume and quantity of work awaiting completion.
- A cycle schedule is a method by which the duration of individual stages and the entire project is measured.
The method is chosen by the manager depending on the economic components. The stage of work, the resources available, etc. influence. These methods can also be used comprehensively, which allows for greater visibility and accuracy of the schedule.
All the methods presented above can be easily created in Microsoft Office, Excel, or other modern planner and organizer programs.
Schedulers
Planner programs will help to significantly simplify the preparation of a plan and the calculation of its parameters. They are effective and relatively easy to use. There are many of them on the electronic products market. Here are just a few:

The presented tools are used in management to create and implement projects. They are multitasking, functional, mobile and work on different platforms.
Regulatory base of the calendar schedule
The main document for planning is the schedule itself. With its help, all design processes are controlled. The schedule becomes the basis for the master plan. The master plan includes:
- Schedules of individual parts of work. Every performer should have them on hand.
- Work package schedules.
- Reports on finances allocated for the implementation of the project.
- Data on resource requirements.
- Plan of organizational measures for the implementation of the project.
- Acts on labor protection.
- Reports on the consumption of resources and materials.
- Progress reports provided by each employee.
- Regulations on the use of equipment.
- When creating certain types of projects, for example, safety documents are required.
A calendar plan is a great planning tool. Using graphic methods and modern programs in its compilation, you can achieve high efficiency. This is important when working on a project. In order for the activity to be regulated and not cause any complaints, all is necessary. Knowledge of the intricacies of planning management is a sign of quality management.
Write your question in the form below